Summary
Wrist Arthroscopy
- Is a keyhole surgery
- Involves inserting a small thin camera called an arthroscope
- Usually performed under a general anaesthesia
Undertaken for
- TFCC tears (triangular fibrocartilage complex)
- Ganglion cysts around the wrist
- To diagnose arthritis in the wrist
- For chronic wrist pain
- Occasionally for fractures
What is an Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is a procedure that allows orthopaedic surgeons to inspect, diagnose and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, Arthro (joint) and skopein (to look). Arthroscopy literally means to look within the joint.
Arthroscopy utilises a small fibre optic instrument called an arthroscope that enables your surgeon to see inside the joint without making a large incision into the muscle and tissue. The camera will then display pictures on a screen and your surgeon will use these images to guide surgical instruments, inspect and repair the problem.
What is an Arthroscopic Wrist Surgery ?
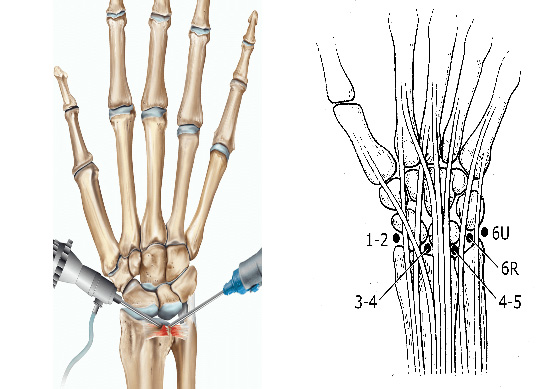
Your wrist is a complex joint with 8 small bones with their connecting ligaments. Wrist arthroscopy is a keyhole surgery that involves inserting a small thin camera called an arthroscope through a small cut in your wrist. Your surgeon will place portals (small cuts) to the back of your wrist in specific locations. This allows your hand surgeon to look inside the two main joints of your wrist and to diagnose and treat wrist injuries and problems using a tiny camera and surgical tools
How long does Wrist Arthroscopic Surgery take?
Wrist arthroscopy is usually performed under a general anaesthesia although it can be done under an arm block. The surgeon will do several small cuts on the back of your wrist joint. The procedure should take between 45 minutes and 1 hour.
What are the indications for Wrist Arthroscopic Surgery?
In my practice I do it most commonly for TFCC tears (triangular fibrocartilage complex). TFCC is a cushioning structure to the ulna side of your wrist. During arthroscopic surgery, the surgeon can repair the TFCC tears or debride them. Other reasons I do a wrist arthroscopy is for a ganglion cysts around the wrist, to diagnose arthritis in the wrist, for chronic wrist pain and occasionally for
fractures.
What is the TFCC in the wrist?
Triangular fibro cartilage complex is a cartilage cushion structure located on the small finger side of the wrist that cushions and supports the small carpal bones in the wrist. A tear to TFCC can happen with a fall on an outstretched hand. This can then result in chronic wrist pain.
How successful is TFCC surgery?
Acute TFCC tears operated within 3 months of injury can give up to 80-90% excellent results with 80- 90% grip strength and range of motion compared to the other wrist. Delayed repair gives less predictable results.
What will happen on the day of surgery?
You will be seen by an anaesthetist who will discuss anaesthetic complications with you. Your surgeon will take you through the consent process. Once you are in the operating room you will be given antibiotics and general anaesthesia.
Surgery involves making several cuts on the back of your wrist from which the camera and arthroscopic instruments are inserted. An assessment is then made of the relevant structures inside the wrist joint. Then depending on the indication for the arthroscopy, treatment is done like removal of loose bodies, removal of any bits of bone or cartilage or inflammed lining of wrist joint, release of capsule, TFCC debridement, ganglion excision, assessment of arthritis etc.
At the end the skin portals will be stitched up and you will come out into recovery in a bulky dressing and a sling.
In my practice, TFCC is the most common indication for which I would offer my patients wrist arthroscopy.
What will happen after Wrist Arthroscopy?
After wrist arthroscopic surgery you will be sent to the recovery room. Your wrist will be covered in a protective bandage and you will be in a sling. You will be in recovery for a few hours and then you will be allowed to go home with pain medication. You will also see a hand therapist on the day of your surgery who will show you range of motion exercises to your wrist and discuss further rehabilitation. The bulky bandage will come off in two days. You will have to keep the wound dry for two weeks at which stage you will see your consultant for a wound check and removal of sutures. Your wrist will improve within 3-6 months depending on the procedure.
What are the complications of Wrist Arthroscopy?
The complications are minimal which may include infection, damage to the skin nerves, swelling, bleeding, stiffness, scarring and occasionally damage to the tendons. These will be discussed with you in the clinic and on the day of surgery and a consent form will be completed with you.
BMI Chelsfield Park Hospital
Bucks Cross Road Chelsfield ORPINGTON BR6 7RG
01689 877855
BMI The Blackheath Hospital
40-42 Lee Terrace Blackheath LONDON SE3 9UD
020 8318 7722
BMI The Sloane Hospital
125 Albemarle Road BECKENHAM BR3 5HS
020 8466 4000
Princess Royal University Hospital
Farnborough Common ORPINGTON BR6 8ND
01689 863223


 info@drsaurabhaggarwal.com
info@drsaurabhaggarwal.com